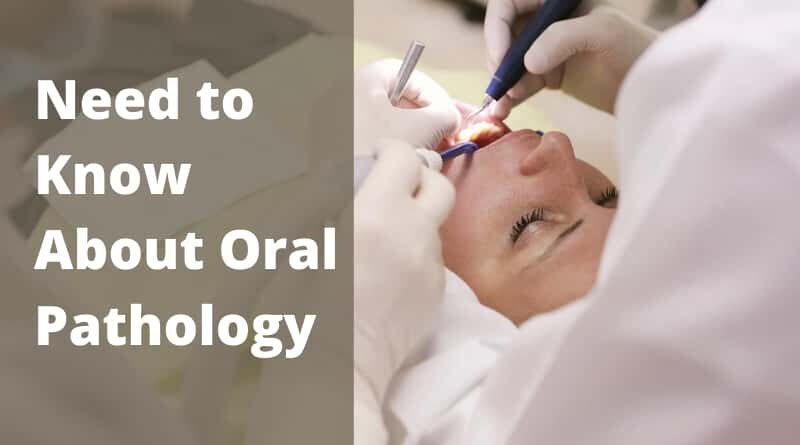
What Do I Need to Know About Oral Pathology?
There’s no denying that we go to great lengths to preserve it when it comes to our oral health. From brushing our teeth to changing our diet, nothing is off the table to protect our beautiful smiles. However, sometimes things go wrong no matter how hard we take care of our teeth. What happens when we have pain, bleeding, or unusual symptoms in our mouth?
Usually, you would visit a local clinic that could handle your dental emergency in Riverdale if you had a problem. But what happens if your dentist can’t figure out what is wrong with your mouth? That’s where oral pathologists come in, diagnosing and assessing a multitude of oral diseases.
Table of Contents
What Is Oral Pathology?
Oral pathology is a branch of dentistry that deals with identifying and managing diseases that affect the oral and maxillofacial areas. In other words, oral pathology tries to figure out both the causes and effects of various oral diseases.
What makes oral pathology unique is the way pathologists assess the disease. Not only do they rely on lab tests and clinical examinations, but they also consider your overall health.
Read: Signs Your Dental Health Needs Attention
Why Is Oral Pathology Important?
Without oral pathologists, it would be almost impossible to diagnose and treat complex oral diseases accurately. For example, let’s say that you are dealing with more gum bleeding than usual. A dentist will know that gum bleeding is an early sign of gum disease, yet he may have difficulty figuring out the cause of the bleeding.
However, a pathologist will consider your health background when making a diagnosis. As a result, the pathologist can notice existing medical conditions or treatments that could interact with your oral health and cause the gums to bleed.
Oral Pathology Diseases
As previously mentioned, oral pathologists handle a variety of diseases that affect the oral and maxillofacial areas. And while many conditions affect those areas, the following are some of the most note-worthy.
Oral Cancer
According to research, almost 50,000 US citizens are diagnosed with oral and oropharyngeal cancer every year. Even though it usually occurs in the mouth, throat, and lips, like any other type of cancer, oral cancer can spread throughout the body. While its leading causes are heavy smoking and alcohol consumption, it can also be caused by other types of cancer present in the body. And without a pathologists’ examination, it can be almost impossible to diagnose oral cancer accurately. Therefore, early prevention and checks are usually the best ways to prevent it from spreading.
Generally speaking, your dentist or doctor will be able to notice the first signs of malignancy during a routine oral exam or cancer screening. Furthermore, if you notice unusual lumps or sores in your mouth, red or white patches on the tongue or even throat soreness, you should see an emergency dentist as soon as possible. After an initial diagnosis, your dentist may send you to an oral pathologist that will do additional examinations and lab tests. Then, the doctor will recommend treatment depending on your medical history and your previous interaction with other medications.
Read: Common Dental Problems
Black Hairy Tongue
The black hairy tongue condition is a common disease that affects many people around the world. Luckily, despite its name, there is no black hair growing on your tongue, even if it looks like there is. To put it simply, the black hairy tongue condition refers to the dead skin cells that collect on the tongue’s surface. Those skin cells can get stained by substances you consume, giving them the appearance of fuzzy, black tissue.
An oral pathologist will be able to take samples from the tongue and prescribe an appropriate treatment. But usually, people dealing with the black hairy tongue disease will first have to eliminate contributing factors such as smoking, consuming alcohol, and drinking soda.
Mouth Ulcers
Mouth ulcers, also known as canker sores, are small and painful lesions at multiple locations inside the mouth. And while some people can confuse them with cold sores, mouth ulcers are not caused by a virus. The leading cause of canker sores is still unknown, with many scientists still debating on it. Yet, some dentists believe that alcohol and smoking contribute to the development of canker sores.
Even though mouth ulcers are not malignant like oral cancer, they can still cause scar tissue formation. As a result, you might start having trouble eating or talking. If this happens, you should visit an oral pathologist as soon as possible. They will be able to rule out cancer and prepare a treatment scheme that can make the sores go away in a matter of weeks.
Read: Acidic Erosion
Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1
Characterized by fever blisters and cold sores in the mouth, herpes simplex virus type 1 (1) is a contagious disease that affects over half of the US population. It can spread through skin contact or saliva from sharing beverages, lip balm, and kissing. And while most people get herpes simplex during their childhood, you can contract it at any age.
The most common symptoms of HSV-1 are the presence of blisters, sores, and a burning sensation around the lips. But since some people can have HSV-1 without showing any signs, it’s hard to diagnose it without a pathologist’s help. And if you already have the disease, a pathologist will prescribe you antiviral creams and medication to reduce the discomfort.
Oral Care Tips
While most, if not all, oral diseases can be treated, it’s hard to deny that prevention is better than cure. The following tips will allow you to maintain good oral hygiene and lower the risk of oral diseases:
- Regular Dentist Checks: You should visit your dentist or local oral pathologist at least twice per year. They will be able to notice early signs of tooth decay, gum disease, and other conditions.
- Brush Your Teeth: Since bacteria and viruses cause most oral diseases, brushing your teeth is essential. Doing it twice a day will remove any leftovers and reduce the chance of plaque formation.
- Avoid Alcohol and Tobacco: As previously noted, alcohol and tobacco are risk factors for multiple pathological oral diseases. Therefore, you should avoid or at least reduce alcohol and tobacco usage.
Conclusion
All in all, oral pathology is an essential branch of dentistry that helps patients avoid and treat various oral diseases. Without an oral pathologist, it would be hard or even impossible to diagnose these conditions, from common infections to cancer.
It’s important to remember that regular dentist and oral pathologist checks can help prevent more serious diseases. As a result, you should visit an emergency dental care clinic as soon as you notice any symptoms. And if found early, even dangerous infections such as oral cancer can be treated in a few weeks or months.